
MCCQE Part 1 Exam
Last Update Feb 28, 2026
Total Questions : 230
We are offering FREE MCCQE Medical Council of Canada exam questions. All you do is to just go and sign up. Give your details, prepare MCCQE free exam questions and then go for complete pool of MCCQE Part 1 Exam test questions that will help you more.



A 31-year-old nulligravid woman presents to your office after 5 months of attempting to get pregnant without success. Her menses are regular, and she is otherwise healthy. Her husband is healthy and has never fathered any children before. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 40-year-old woman presents to your clinic for follow-up regarding her major depressive disorder, which is being treated with the starting dosage of escitalopram. Most of her symptoms have now improved. However, she has noted anorgasmia since taking this medication. This has significantly affected her relationship with her wife. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A health authority implements the first-ever colon cancer screening program in its territory. Which one of the following colon cancer indices will likely increase?
A 2.5-year-old boy is brought to the Emergency Department after he consumed a button-shaped battery. Chest and abdomen radiographies are performed. Which one of the following locations mandates urgent removal of the battery?
You are evaluating a 75-year-old man with recently diagnosed prostate cancer and 2 painful metastases of the lumbar spine. Which one of the following therapeutic options is the most appropriate?
You are covering for your colleague who is on vacation this week. You receive the results from an ultrasonography that had been ordered for a 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, aborta 0. The ultrasonography-estimated fetal weight is below the fifth percentile for 30 weeks' gestation; gestational age was confirmed by an earlier ultrasonogram. The amniotic fluid volume is within normal range. Her first child's birth weight was 2800 g at full term. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 62-year-old man (wealthy philanthropist) with emphysema from smoking and a 21-year-old woman (elementary teacher) with cystic fibrosis are both compatible matches for a lung transplant. Which criterion determines organ allocation?
You are asked to see a 50-year-old man 2 hours after he underwent a laparotomy for gastric resection. Lab results are as follows:
pH
7.28 (7.35–7.45)
PaCO₂
60 mm Hg (35–40)
PaO₂
60 mm Hg (85–105) with 4 L/min via nasal prongs
Bicarbonate (HCO₃)
24 mmol/L (24–30)
Which one of the following is most consistent with this clinical presentation?
A 42-year-old man presents with a history of fatigue and weight loss. He looks unwell, has a darker than usual complexion and his liver is enlarged. He is also found to have marked glycosuria. Which one of the following is the most useful diagnostic test?
A 3-week-old boy is brought by his parents to your clinic for a well-child visit. The newborn was born at term after an uncomplicated pregnancy. He is exclusively breastfed and is thriving. Physical examination findings are normal except for jaundice. Total bilirubin is 172 μmol/L (≤100), and conjugated bilirubin is 4 μmol/L (≥5). Results of a complete blood count and reticulocyte count are within the normal range. The results of a direct antiglobulin (Coombs) test were negative. Which one of the following, if any, is the most appropriate investigation?
A 32-year-old primigravid woman is receiving magnesium sulfate for tocolysis. Her pregnancy is at 26 weeks' gestation. You suspect magnesium sulfate toxicity. Which one of the following is the first sign of magnesium sulfate toxicity?
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 1, aborta 0, gave birth to a newborn who is hypotonic with a large protruding tongue and brachycephaly. The newborn has a single palmar crease bilaterally and short, broad hands with a curved fifth digit. These features best support a clinical diagnosis of which one of the following?
A 62-year-old woman is referred to your clinic for evaluation of hypercalcemia. She has a history of hypertension and vitamin D deficiency. Her medications include hydrochlorothiazide and vitamin D supplements. Laboratory investigations are as follows:
Calcium: 2.72 mmol/L (↑)
Phosphate: 0.9 mmol/L (↓)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH): 0.9 pmol/L (↓)
25-hydroxy vitamin D: 80 nmol/L (normal)
Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 12-year-old girl presents to your office in late November with an exacerbation of asthma which has been well controlled since her diagnosis at age 5. The family has had cats for 3 years. Last June, they moved to a basement apartment. Which one of the following is the most likely cause of her asthma exacerbation?
You are counselling the wife of a 75-year-old man admitted under your care after a fall. The patient is confused, disoriented, barely sleeps at night and has complex visual hallucinations of animals running through his room. Given his state, which one of the following is the best advice for the wife?
A 54-year-old woman presents to your office to discuss breast cancer screening. She is asymptomatic with no history of breast cancer. She had a fibroadenoma removed when she was 24 years old. The patient is not on any medications. Her family history is significant for a great-aunt with breast cancer. The patient has not had genetic testing but had normal breast screening 2 years ago. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 53-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with a 3-week history of believing his neighbor is poisoning him by pumping gas through his home’s air vent. He appears distracted, irritable, and is speaking very quickly. He has a family history of depression. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Your colleague's receptionist asks you to assess her 4-year-old daughter who has had 2 episodesof acute otitis media in the last month. The mother wants you to arrange a consultation with an ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist to get a tympanostomy before her daughter starts school. You do not believe there is a surgical indication at this time. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 52-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with a history of back, neck, and shoulder pain sustained from a workplace incident 4 years ago. He is under observation by a multidisciplinary pain clinic, and his next appointment is not for another 4 weeks. He does not report any recent change in his symptoms. His medications are as follows:
Acetaminophen
1000 mg orally 4 times daily
Naproxen
500 mg orally twice daily
Amitriptyline
25 mg orally at bedtime
Acetaminophen 1000 mg orally four times daily
Naproxen 500 mg orally twice daily
Amitriptyline 25 mg orally at bedtime
The patient has not taken his medications for several weeks because he thinks they are not working. He requests a prescription for oxycodone because he tried some that a friend sold him, and it worked very well. After completing an assessment and providing counseling, which one of the following is the best next step?
A 62-year-old woman is taken to the operating room for an elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Induction of anesthesia triggers a severe hypertensive crisis that ultimately resolves after administration of a 5 mg bolus of phentolamine.
Which one of the following is most consistent with this presentation?
An otherwise well 18-month-old girl is brought to your family practice office for routine immunization. Her mouth is as shown in the attached image. She has no symptoms. Which one of the following is the most likely cause of this presentation?
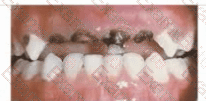
Image description: Severe black and brown decay of multiple upper front teeth, with relatively spared lower teeth.
A 42-year-old man presents to your clinic for follow-up regarding his anxiety. He lost his job 1 year ago. Since then, he constantly thinks about what happened, trying to understand what went wrong and how he could fix it or prevent it in the future. He is unable to sleep because of this. He has become socially isolated and when he does see friends, he worries constantly that he may say something hurtful. He wishes he could get past what happened and find another job but feels consumed by the fear that he may offend someone in the future. On history, his symptoms did not respond to escitalopram, sertraline, fluvoxamine, or venlafaxine, all at maximum tolerated doses. Which one of the following medications is the most appropriate?
You are called to the Emergency Department to see a 6-month-old boy with a 3-day history of fever. Physical examination reveals an irritable infant with a temperature of 38.1°C. His vital signs are:
Blood pressure: 87/50 mm Hg
Respiratory rate: 80/min
Heart rate: 140/min
Oxygen saturation: 92% on room air
The infant has no skin findings. On chest examination, you hear coarse crackles on the right side of the chest. Which one of the following is the best next step in the management of this child?
You are treating a 78-year-old man for recent onset of diarrhea, tenesmus, and minor bleeding when he wipes. He has a history of prostate cancer that was treated by radiotherapy. Rectal examination findings are normal. Colonoscopy reveals a pale rectum with ulcerations and areas of mucosal hemorrhage. Which one of the following is the most likely explanation for this clinical presentation?
You are meeting an otherwise healthy 10-year-old boy in your office for the first time. His BMI is at the 80th percentile. He has no symptoms and his physical examination is normal. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A mother brings her 13-year-old daughter to the office. The girl has had intermittent lower abdominal pain, constipation, and difficulty voiding for 3 months. She says that she is not sexually active. She looks well. She has reached age-specific developmental milestones, and her vital signs are within normal range. On abdominal examination, she is found to have a palpable suprapubic mass that persists after voiding. The girl says that her older sister started having menstrual periods at this age. The patient is surprised that hers have not started. Which one of the following is the best next step?
An 84-year-old woman is brought by ambulance to the emergency department after she was found by a neighbour. She had fallen, sustained a hip fracture, and was unable to move for the past 2 days. After starting rehydration, she reports hip pain and numbness and tingling in both her legs. Physical examination reveals faint pulses in both legs and severely swollen lower legs that are painful to palpation. The urine in the Foley catheter bag seems to be darker than normal. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 35-year-old woman presents to your clinic with double vision and a gritty sensation in her eyes for the past several weeks. On examination, you notice her eyes are bulging. There is inflammation of her conjunctivae and swelling around her eyes. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 42-year-old woman is admitted to the Intensive Care Unit with a massive pulmonary embolism. Her condition is stabilized with intubation, hydration, inotropic support, and intravenous administration of heparin. Her partner provides you with a list of her medications. A combination oral contraceptive pill was recently prescribed. She smokes tobacco cigarettes, and her BMI is 36. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 43-year-old man is referred to you for an incidental finding of elevated hemoglobin. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin
185 g/L (130-170)
Mean corpuscular volume
92 fL (60-100)
White blood cells
7.8×1037.8×103 / L (4-10)
Platelets
250×103250×103 / L (130-400)
His BMI is 23. He has type 2 diabetes for which he takes gliclazide MR 60 mg daily. Which one of the following features on history could explain his laboratory abnormality?
A 67-year-old man underwent his first endoscopy. He has long-term reflux and heartburn, treatedintermittently with antacids. Biopsies of the distal esophagus reveal Barrett epithelium. Which one of the following is most important in determining the frequency of surveillance endoscopy?
A 44-year-old woman presents to the office to discuss contraception. During the gynecologic examination, you notice an anterior cystocele to the hymenal ring. The woman denies any bulge symptoms but does report dribbling of urine, especially when she coughs or jogs.
Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 64-year-old man presents with a 3-month history of gradually increasing neck pain and stiffness. The pain radiates into his upper back, and he is having difficulty driving because of limitation of neck rotation secondary to pain. Physical examination shows restricted neck motion in all directions and neck muscle spasms. There is no abnormality on neurologic examination. A radiograph shows narrowing of all of the cervical disc spaces with prominent osteophytes. Which one of the following is the most appropriate next step?
You performed a surgical procedure on a 32-year-old woman for a herniated disk that was causing neurologic impairment. At the 8-month follow-up visit, she has healed well; however, she requests a prescription renewal of her narcotic analgesics (hydromorphone). Her pharmacy confirms that the patient adheres to the dosage you prescribed, that she has not consulted other physicians, and that her behavior has always been respectful. You think that she no longer requires narcotic analgesics. Which one of the following approaches is most helpful to the patient?
A 30-year-old man (assigned female at birth) presents to your clinic for a periodic health examination. He declines a gynecologic examination because such examinations lead to intense emotional distress for him. He also believes that he does not require a Papanicolaou (Pap) test because he is not in a sexual relationship with a man. After acknowledging the patient's distress and providing education regarding the need for Pap screening, which one of the following would be the best next step?
A 14-year-old girl, accompanied by her mother, presents to your office with a 3-month history of feeling "dizzy." After you take an initial history, which one of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A 21-year-old man presents to the office with persistent pain and swelling of the wrist 2 weeks after falling on his outstretched hand. Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the wrist taken at the time of the injury showed no evidence of fracture or dislocation. Which one of the following is the most likely cause of the patient's symptoms?
A 66-year-old woman suffering from a progressive neurological disease is admitted to a long-term care centre. Her husband does not wish to participate in discussions about the seriousness of his wife's disease and is convinced that she will soon come back home. During his 2nd visit to the centre, he gives you a cheque for a substantial sum made out to you, the treating physician, for your own research. Which one of the following is the best response to your patient's husband?
A 6-week-old boy is brought to your office by his parents for a follow-up following a recent urinary tract infection. His abdominal ultrasound shows dilated urinary bladder and ureters as well as bilateral hydronephrosis. Which one of the following historical findings would be most helpful in establishing the correct diagnosis?
You are examining a newborn in the delivery room. He was born at full term by spontaneous vaginal delivery. On examination, he is active, and his vital signs are within normal range. His head circumference is at the third percentile, with height and weight at the 10th percentile. Auscultation of his chest is clear with normal cardiovascular examination findings. The abdomen is protuberant with a liver edge palpable at 4 cm below the costal margin and mild splenomegaly. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
An 80-year-old woman presents to your office with weight loss and generalized weakness. Her husband calls you after the appointment and asks that his wife not be told if she is diagnosed with cancer as hearing this will likely "kill her." Investigations subsequently show that she has metastatic lung cancer. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 60-year-old man has a strong family history of aortic aneurysms. Screening abdominal ultrasonography reveals an incidental <1 cm mass in his left kidney. Computed tomography confirms that the mass is consistent with renal adenocarcinoma. Which one of the following is the most appropriate step in management?
A 60-year-old man presents to the office with concerns regarding a pruritic rash, which he has had for several years. He reports a “crawling” sensation on his skin. He is concerned that this rash may be caused by a parasite he may have picked up while serving in the military overseas. On examination, you note multiple crusted lesions on his forearms, neck, chest, scalp, and thighs. There is a complete sparing of the skin on his back. He brought a bottle with fibrous material of different colours that he picked from his wounds. He is otherwise healthy and reports no other symptoms except some chronic fatigue and insomnia related to the itching. Which one of the following treatments is the most appropriate?
A 40-year-old woman presents to the Emergency Department with confusion and fever (38.5°C). She has a history of hypothyroidism managed with levothyroxine. Key findings include:
Blood pressure
114/78 mm Hg
Heart rate
85/min
Temperature
38.5°C
Hemoglobin
90 g/L123-157 g/L
Platelet count
25 × 10⁹/L130-400 × 10⁹/L
Peripheral blood film
Schistocytes present
Creatinine
200 μmol/L50-90 μmol/L
A 70-year-old woman consults you for progressive vision problems. She describes seeing haloes at night around street lights and having double vision. Her near vision has improved. Which one of the following is an ophthalmologic examination most likely to uncover?
A same-sex couple asks to join a family physician’s practice. The physician tells them that shedoes not treat same-sex couples and will refer them to a physician with more clinical experience with same-sex couples. Which one of the following best describes the physician’s obligation under the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms?
A 35-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 0, aborta 3, presents with her male partner because she has been unable to conceive despite trying for more than 1 year. Her menstrual cycles have been absent for 9 months, and she has occasional mild cyclic pain. She has a medical history of 3 suction curettages. Her BMI is 24. Investigation results are as follows:
Hysterosalpingogram: Obliterated uterine cavity, no tubal dye spill
Progesterone (midluteal): 48.0 nmol/L (16.4–59.0)
Partner's semen: All parameters normal
Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 72-year-old man reports that his wife says he has hearing trouble. Examination reveals that air conduction on the right side is less than on the left side and greater than bone conduction bilaterally. He hears a tuning fork placed on the top of his head better with his left ear. Which one of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
You are travelling on a transatlantic flight. Halfway through the flight, an older passenger (≥ 65 years) begins to have chest pain and shortness of breath. An announcement is made over the intercom asking for help from any physicians or medical personnel. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 59-year-old woman is referred to you because of a 2-month history of left nipple discharge. She is otherwise healthy and is not on any medication. There are no palpable lesions on breast examination. She is able to express a small amount of blood-tinged liquid from her breast. Which one of the following would be the best next step?
A 40-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a 24-hour history of severe abdominal pain and recurrent vomiting. He has a long-term history of alcohol use disorder. His blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, and his heart rate is 120/min. The pain is located mostly in the epigastrium but radiates to the right upper quadrant and to his back. Radiographs of the abdomen and chest reveal some distended small bowel loops in his upper abdomen. Laboratory work results are pending. After fluid resuscitation, which one of the following is the best next step?
You are working in a busy family practice. Your colleague's 48-year-old female patient presents with a 6-month history of fatigue and gastrointestinal symptoms. A recent colonoscopy was normal. Her chart indicates multiple investigations for similar symptoms over the past 2 years, all of which have been non-revealing. Your working diagnosis is somatic symptom disorder. Which one of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
A 22-year-old woman presents to the office for episodic mood changes that her boyfriend has noticed. During such episodes, she cries suddenly, is irritable and sad, and withdraws from socializing. Which one of the following would be most useful in establishing a diagnosis?
A 27-year-old woman presents to her family physician's office and states that she is pregnant and would like to be referred for an abortion. She is at approximately 9 weeks' gestation by dates. The family physician has personal conscience-based objections to the procedure. Which one of the following would be the best next step for this physician?
A 37-year-old woman presents to your clinic with frequent palpitations. She has no other symptoms and is quite active. Physical examination and resting electrocardiogram findings are normal. Which one of the following is the best next step?
Three months ago, a physician colleague approached you in the hospital corridor for advice regarding one of his patients. You are now being named by this patient in a malpractice action. Which one of the following is the most likely reason why you may be found liable?
A 55-year-old woman presents to the office with a 2-month history of right shoulder pain and limited function that started after she began an upper body weight training program. Examination shows tenderness inferior to the acromion. She has full passive range of motion of the shoulder but significant pain with abduction from 30° to 120° of arc. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 58-year-old woman presents to your office with heavy vaginal bleeding. She has a history of type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Some active bleeding is visible on speculum examination. Ultrasound reveals an endometrial thickness of 12 mm. Endometrial biopsy shows complex hyperplasia with atypia. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 29-year-old man comes to the office for an initial visit. He is being treated for schizophrenia and epilepsy. He has a 20 pack-year history of smoking. His medications are carbamazepine, clozapine, and quetiapine. In the past year, he has gained a considerable amount of weight. Asidefrom a BMI of 32, the results of his physical examination are unremarkable. Which one of the following conditions should he be investigated for?
A 33-year-old man with severe bacterial meningitis is intubated and unresponsive in the Intensive Care Unit. If he receives immediate treatment, his prognosis is excellent. If he does not, he will likely die. Three years ago, the patient had Huntington disease diagnosed, but he has been asymptomatic since then. His advance directive, which was made before this hospitalization, states that he should be allowed to die if he contracts a life-threatening illness. His parents demand that he be treated for the meningitis. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 24-year-old man presents to your clinic with a 6-month history of fatigue. On examination, he is pale. His BMI is 16, and his blood pressure is 92/58 mm Hg. Initial laboratory work shows the following:
Creatinine: 64 µmol/L (49–93)
Potassium: 3.0 mmol/L (3.5–5.1)
Sodium: 138 mmol/L (136–146)
TSH: 2.40 mIU/L (0.34–5.60)
CBC: Normal
Which one of the following is the best next step?
You are being consulted for a 79-year-old man who is about to undergo a total hip arthroplasty. His orthopedic surgeon is aware of the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease and would like your suggestions to help avoid acute postsurgical delirium. To that end, which one of the following is the most effective strategy?
An intoxicated 28-year-old man is brought to the Emergency Department after being found in the snow. His vital signs are as follows:
Temperature: 33°C
Respiratory rate: 22/min
Heart rate: 123/min
The patient is shivering and displays some dysarthria and ataxia. After his wet clothing is removed, he is provided with a warm blanket. The results of the subsequent physical examination are unremarkable, except for frostbite of the ears and fingers. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A mother brings her previously healthy 4-month-old girl for evaluation due to fussiness for 3 weeks. The infant becomes irritable and cries with occasional body arching 1-2 hours after feeding, frequently spits up after feeds, has developed feeding aversion, and shows slowing weight gain. She has been on cow's milk-based formula since birth. Stools are normal, and physical examination is unremarkable. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 12-year-old boy initially presents with a 4-month history of left knee pain. He denies any obvious history of trauma, but he plays basketball frequently and notes his pain is worse after playing. On physical examination the patient has a prominent tibial tubercle, which is swollen and tender. There is full range of motion in the knee. A radiograph of the left knee reveals an ossicle anterior to the tibial tuberosity. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 30-year-old woman presents to the office with her partner and reports that they are planning for her to conceive soon. They visited Mexico recently and are concerned about exposure to the Zika virus. Which one of the following is the best next step?
One of your patients presents to your clinic for a consultation regarding their recurrent hemoptysis. On review of their chart, you realize that although you had ordered chest radiography 2 months ago, the result cannot be found in the chart. You call the radiology department and are relieved to find that the chest radiography was done and that it did not reveal any pathology. After informing the patient of this lapse in reporting, which one of the following is the best next step?
A 34-year-old man sustained a blunt testicular trauma 2 hours ago. On physical examination, the patient has a 1.5-cm tall scrotal hematoma. You cannot palpate the testicle. Which one of the following is the best initial management?
A 55-year-old woman presents with a 6-month history of poor memory and impaired concentration. She has bipolar I disorder that has been treated with lithium carbonate for 4 years. She has gained a lot of weight since starting lithium. Physical examination findings are otherwise normal. She is concerned about her memory issues, but there are no other perception, mood, or cognition abnormalities. Which one of the following tests is most likely to have abnormal findings?